What is it about?
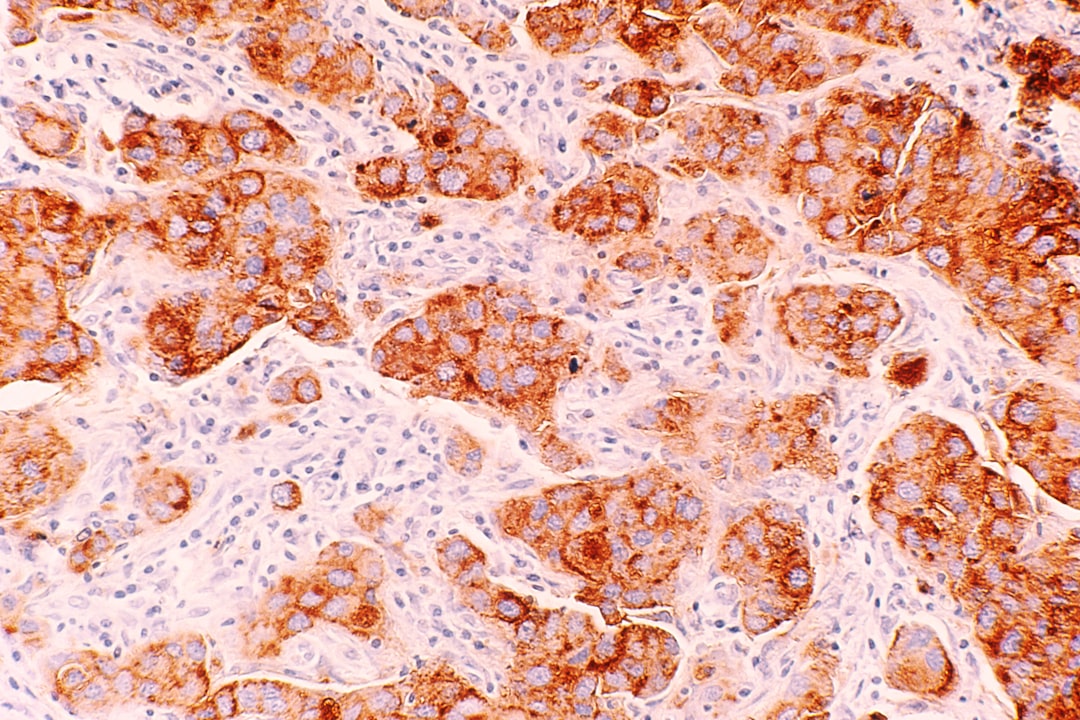
Context: Gastric ghrelin-positive endocrine cells (GHRþEC) were most dense in the oxyntic mucosa. Objective: We evaluated ECs and contractile activity in rat stomach with metabolic disorders. Materials and methods: Male Wistar rats were divided into two groups: Control (n¼9) received tap water and Fructose (n¼9) drank 15% fructose solution for 12 weeks. Streptozotocin was applied in a dose of 20 mg/kg b.w. two weeks after the beginning of the experiment on Fructose group. Smoothmuscle strips from the stomach were influenced by Angiotensin II for analysis of parameters of contractions. Stomach samples were elaborated with immunohistochemistry for ghrelin, somatostatin, gastrin antibodies and with double immunofluorescence. Results: In treated animals, GHRþEC were significantly increased in the corpus where somatostatinpositive cells were decreased. Contractile activity was decreased. Conclusions: The increase number of GHRþEC was discussed in the context of Somatostatin and Gastrin-positive ECs variations and correlated with the decrease of smooth muscle contraction.
Featured Image

Photo by David Clode on Unsplash
Why is it important?
The increase number of GHRþEC in the context of Somatostatin and Gastrin-positive ECs variations and correlation with the decrease of smooth muscle contraction.
Perspectives
To enlarge the knowledge about Ghrelin and its influence on the smooth muscle contractions.
Anna Tolekova
Trakijski Universitet Stara Zagora
Read the Original
This page is a summary of: Fructose-induced metabolic disturbances in rats and its impact on stomach endocrine cell number and smooth muscle contractility, Archives of Physiology and Biochemistry, January 2019, Taylor & Francis,
DOI: 10.1080/13813455.2018.1555601.
You can read the full text:
Contributors
The following have contributed to this page