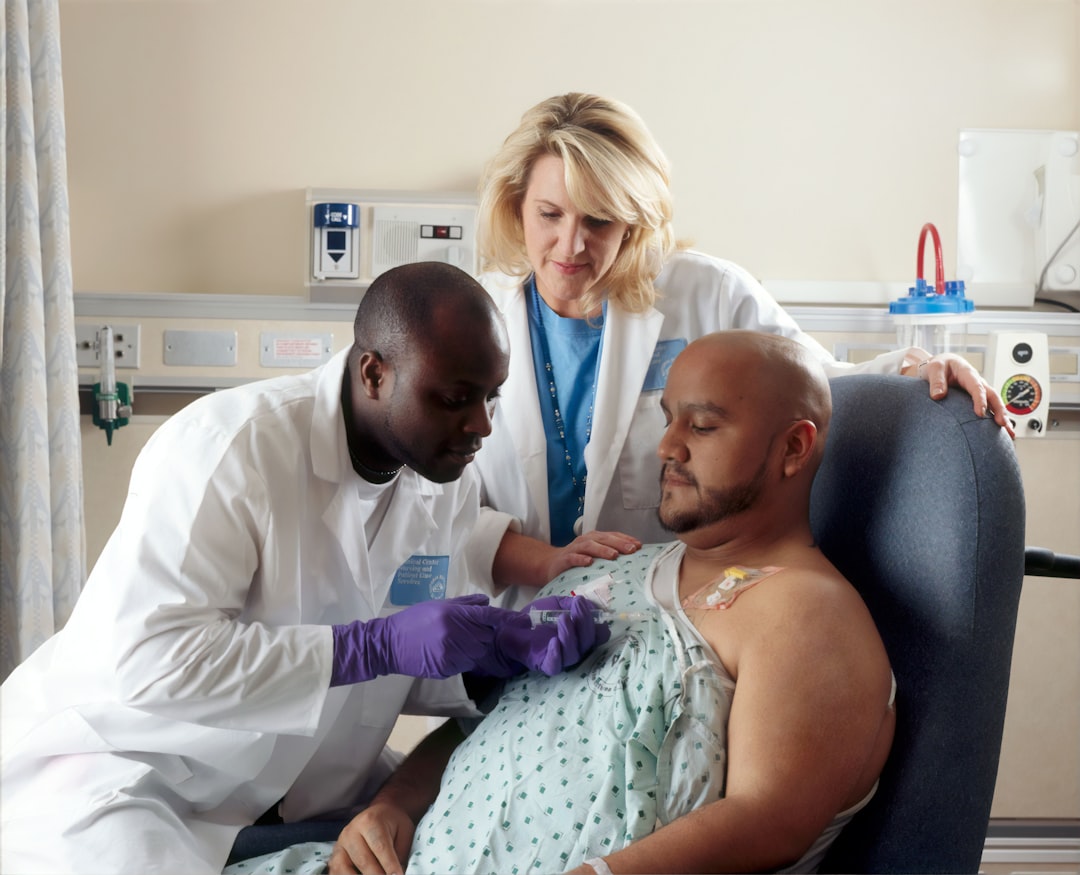
What is it about?
This study examined the use of vitamin E to alleviate toxic effects of sodium selenite. Adult male albino rats (n = 50) was divided into five groups. Group 1 was control, Groups 2 and 4 were treated with sodium selenite (2 mg/kg) for 2 and 4 weeks, respectively, Groups 3 and 5 were treated with sodium selenite (2 mg/kg) and vitamin E (100 mg/kg) for 2 and 4 weeks, respectively. Renal tissues were studied using anti-BCL2 and examined ultrastructurally. Positive Bax immunoreactivity was detected
Featured Image
Why is it important?
Present findings disclosed an ameliorative effect of adding vitamin E to sodium selenite-induced changes in cortical tissues. Clinically, it is advised to add vitamin E to avoid selenium overdose hazards.
Perspectives
This study examined the use of vitamin E to alleviate toxic effects of sodium selenite. Adult male albino rats (n = 50) was divided into five groups. Group 1 was control, Groups 2 and 4 were treated with sodium selenite (2 mg/kg) for 2 and 4 weeks, respectively, Groups 3 and 5 were treated with sodium selenite (2 mg/kg) and vitamin E (100 mg/kg) for 2 and 4 weeks, respectively. Renal tissues were studied using anti-BCL2 and examined ultrastructurally. Positive Bax immunoreactivity was detected
Prof. Hesham N. Mustafa
King Abdulaziz University
Read the Original
This page is a summary of: Effect of Sodium Selenite and Vitamin E on the Renal Cortex in Rats: An Ultrastructure Study, Tissue and Cell, June 2014, Elsevier,
DOI: 10.1016/j.tice.2014.03.002.
You can read the full text:
Resources
Contributors
The following have contributed to this page