What is it about?
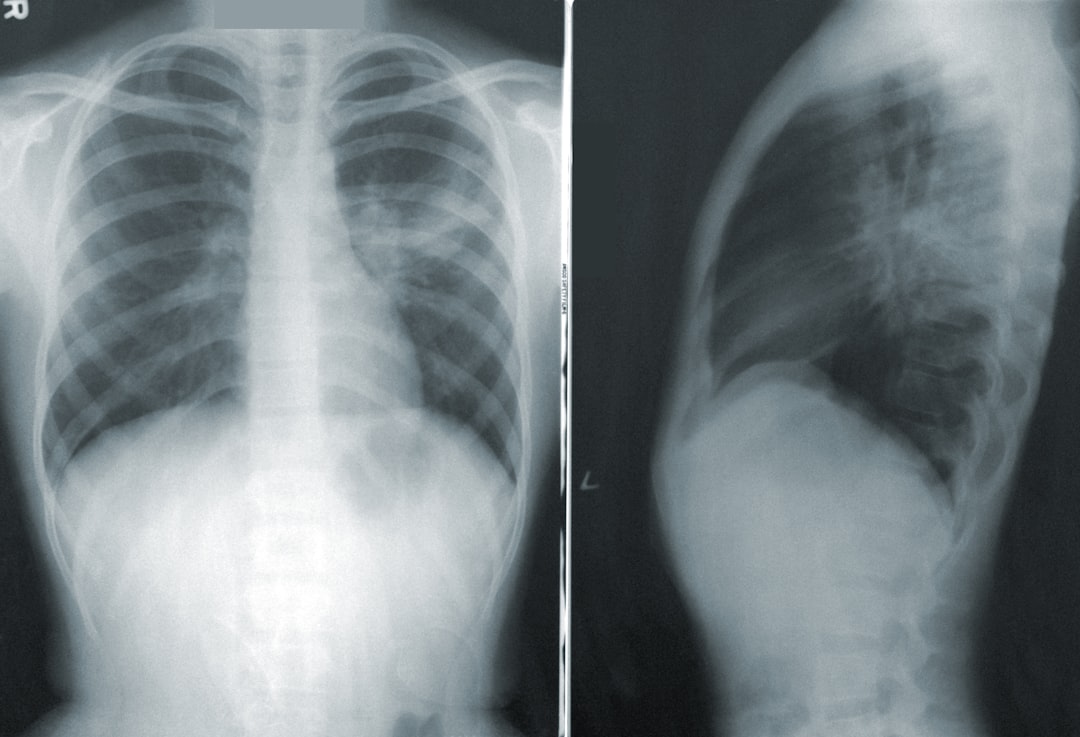
The main pathological syndrome of coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19) is an severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Recently, however, many researchers have drawn attention to a significant coagulation imbalance in COVID-19 patients, confirmed by laboratory findings as well as postmortem data. The number of studies on coagulopathy in COVID-19 patients with SARS-CoV-2 is limited. Also, there are currently no studies that would analyze von Willebrand factor (vWF) activity in these patients at critical stage.
Featured Image
Photo by CDC on Unsplash
Why is it important?
Increased fibrinogen and D-dimer levels indicate that COVID-19 patients are in a state of hypercoagulation. In all patients, also a significant increase in vWF activity was observed. The increase in vWF activity reflects the of vascular endothelial damage in COVID-19 and may be one of the important causes of coagulation disorder in these patients.
Perspectives
vWF activity may be used to develop new approaches to assess the severity of hemostasis disorders while COVID-19. It is also likely that the vWF may be a target for monoclonal antibody therapy or protease specific therapy.
Alexander Osipenko
Mogilev State A. Kuleshov University
Read the Original
This page is a summary of: Blood coagulation parameters and von Willebrand factor activity in critical stage COVID-19 patients, Acta Haematologica Polonica, April 2021, VM Media SP. zo.o VM Group SK,
DOI: 10.5603/ahp.2021.0021.
You can read the full text:
Contributors
The following have contributed to this page