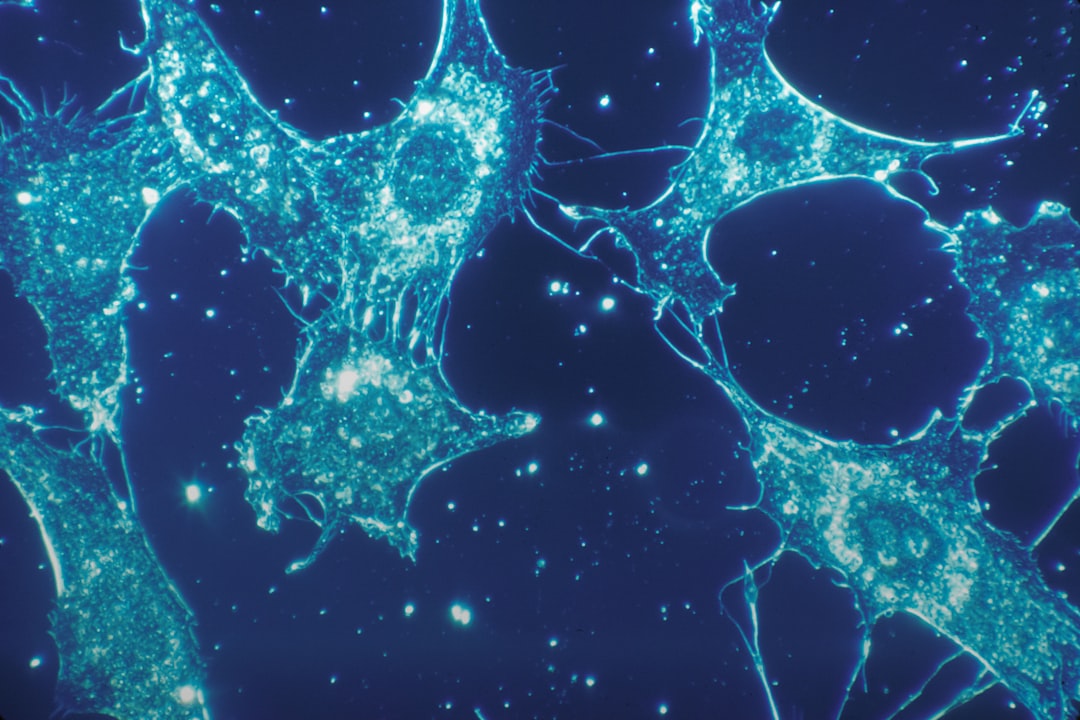
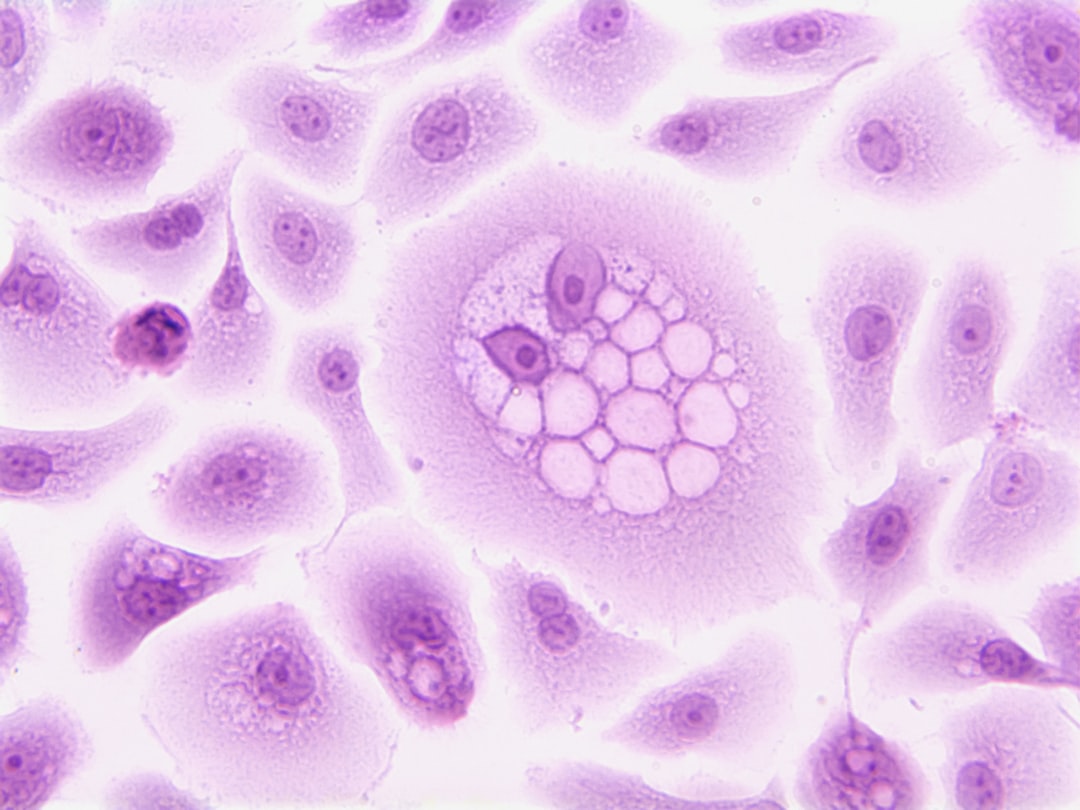
What is it about?
The present study evaluated the effects of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 2 and epidermal growth factor (EGF) on proliferation and the expression of some genes in spermatogonial cells. Spermatogonial cells were isolated from prepubertal buffalo testes and enriched by double enzyme treatment, filtration through 80- and 60-μm nylon mesh filters, differential plating on lectin-coated dishes and Percoll density gradient centrifugation. Cells were then cultured on a buffalo Sertoli cell feeder layer and formed colonies within 15–18 days. The colonies were found to predominantly contain undifferentiated Type A spermatogonia because they bound Dolichos biflorus agglutinin and did not express c-kit. The colonies expressed alkaline phosphatase, NANOG, octamer-binding transcription factor (OCT)-4 and tumour rejection antigen (TRA)-1–60. Cells were subcultured for 15 days, with or without growth factor supplementation. After 15 days, colony area and the relative mRNA abundance of PLZF were higher (P < 0.05) following supplementation with 40 ng mL–1 GDNF + 10 ng mL–1 EGF + 10 ng mL–1 FGF2 than with the same concentrations of GDNF alone or GDNF plus either EGF or FGF2. Expression of TAF4B was higher (P < 0.05) in the presence of FGF2, whereas the expression of THY1 was not affected by growth factor supplementation. In the Sertoli cell feeder layer, EGF and FGF2 decreased (P < 0.05), whereas GDNF increased (P < 0.05), the relative mRNA abundance of ETV5 compared with control.
Featured Image
Why is it important?
Fertility preservation and conservation of endangered species
Perspectives
In conclusion, an in vitro culture system that incorporates various growth factors was developed for the short-term culture of buffalo spermatogonia.
Dr Prashant H Kadam
Vrije Universiteit Brussel
Read the Original
This page is a summary of: Effects of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor, fibroblast growth factor 2 and epidermal growth factor on proliferation and the expression of some genes in buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) spermatogonial cells, Reproduction Fertility and Development, January 2013, CSIRO Publishing,
DOI: 10.1071/rd12330.
You can read the full text:
Contributors
The following have contributed to this page