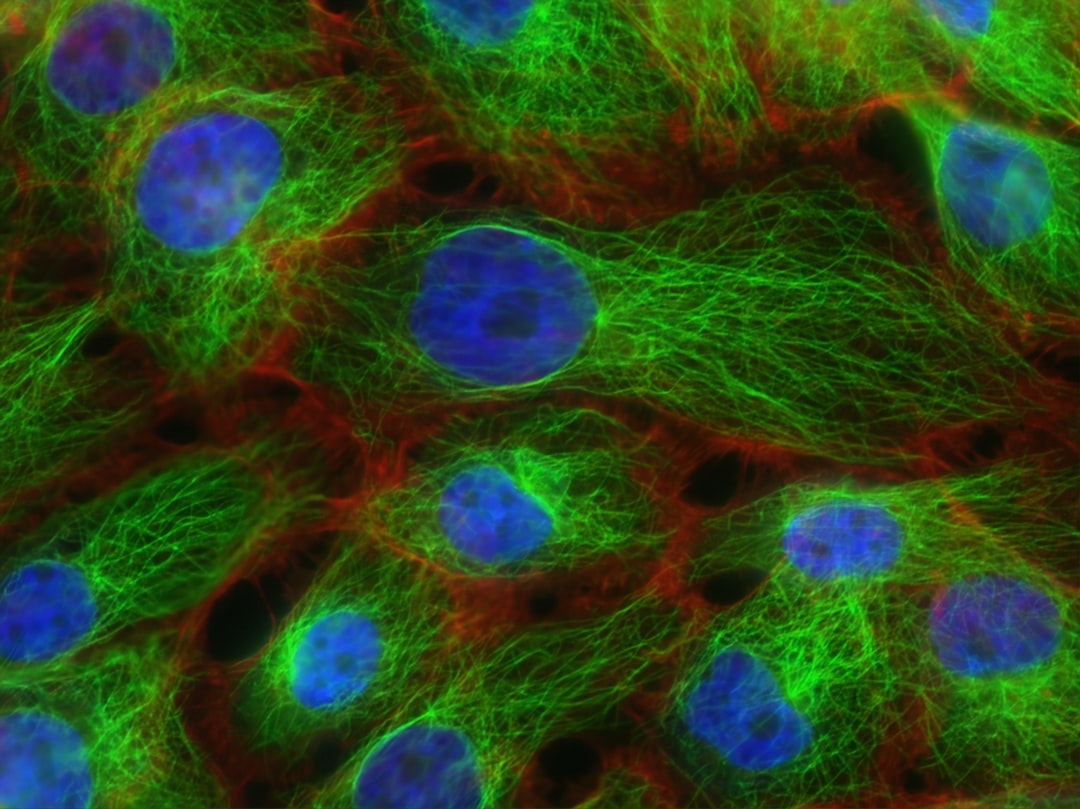
What is it about?
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common form of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. R-CHOP is currently the standard therapy for DLBCL, but the prognosis of refractory or recurrent patients remains poor. We synthesized a new water-soluble anti-malarial drug artemisinin derivative, SM1044, confirmed its effectiveness in treating DLBCL, as well as elucidated the mechanismof SM1044 in this paper.
Featured Image
Why is it important?
Our research reported an Artemisinin derivative, SM1044, induces autophagy-dependent apoptosis which triggered by an increased acetylation of Survivin, a modification which induces its interaction with LC3-II and its degradation. We also unraveled that the activation of CaMKK2-AMPK-ULK1 axis was molecular basis of SM1044-dependent stimulation of autophagy. These investigations not only point to SM1044 as a promising molecule in fighting DLBCL, but also unravel important information of the molecular pathways involved in the oncogenesis of DLBCL.
Perspectives
A new artemisinin derivative SM1044 is a promising therapeutic molecule for the treatment of DLBCL.
chunyan cheng
Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Read the Original
This page is a summary of: Induction of autophagy and autophagy-dependent apoptosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by a new antimalarial artemisinin derivative, SM1044, Cancer Medicine, December 2017, Wiley,
DOI: 10.1002/cam4.1276.
You can read the full text:
Contributors
The following have contributed to this page