What is it about?
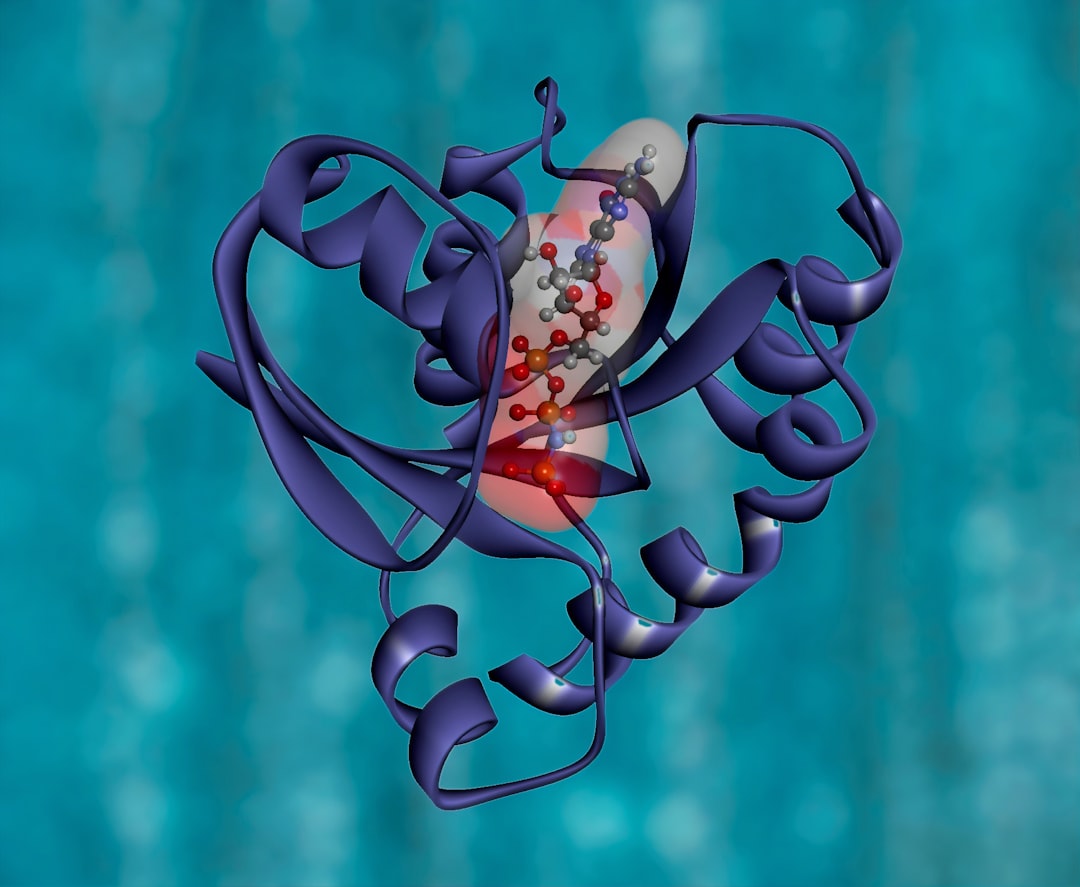
The present work explores the interaction of photodynamic therapeutic (PDT) agent thionine (TH) with bovine serum albumin (BSA) using absorption, emission, synchronous emission, circular dichroism (CD) and three-dimensional (3D) emission spectral studies. Experimental results demonstrate that TH quenches BSA through static quenching mechanism. The molecular docking study further substantiates Sudlow site I as the preferable binding site of TH in BSA.
Featured Image
Why is it important?
Binding studies between dyes and BSA are available in the literature. However, a site-specific interaction of dyes with BSA find little mention in the previous literature reports. Further, In view of the enormous range of applications of TH, it is necessary to understand the binding mechanismof TH with biological systems to elucidate their potential applications and toxic effects on biological macromolecules. Hence, in the present investigation, we have explored the binding interaction between TH and BSA using multi-spectroscopic studies.
Perspectives
This results of this study provide a deep understanding of the site-specific interaction of BSA with TH. The in situ knowledge thus obtained may provide useful insights in developing new photoactive drugs.
Mr Manivel P
Bharathiar University
Read the Original
This page is a summary of: Exploring the interaction of the photodynamic therapeutic agent thionine with bovine serum albumin: multispectroscopic and molecular docking studies, Luminescence, November 2014, Wiley,
DOI: 10.1002/bio.2812.
You can read the full text:
Contributors
The following have contributed to this page